On Dec 23, 2020, the research group led by Prof. Xia Baoyu from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of HUST published a research paper entitled "Local Spin-State Tuning of Cobalt-Iron Selenide Nanoframes for the Boosted Oxygen Evolution" on
Energy & Environment Science
. This research group focuses on the research of service and failure of energy materials. This work marks the
latest research progress in spintronics of highly efficient cobalt-iron selenide oxygen evolution catalysts. It demonstrates a highly efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalyst and may pioneer a promising approach which involves tuning the local electronic structure to achieve the improved electrocatalysis activities in energy conversion technologies. Huazhong University of Science and Technology is the signature unit of the first author, and Prof. Xia Baoyu from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering is the corresponding author of the paper.
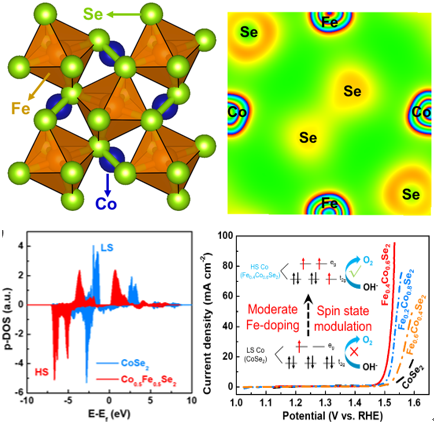
Electrochemical water electrolysis is regarded as a promising approach for sustainable hydrogen production. However, its scalable application is greatly limited by the sluggish kinetics of the anodic oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Consequently, developing highly active electrocatalysts is significant yet challenging for boosting the inferior OER activity. Recently, transition metal compounds with high-valence cobalt active sites have demonstrated their potential in promoting OER. Subsequently, the formation strategies and modulation mechanisms of high-valence cobalt active sites have attracted much attention in developing efficient OER electrocatalysts. Herein, a simple selenization method to prepare hollow cobalt selenides and an effective strategy of utilizing higher spin states of Co species to improve the OER activity of the low-cost CoSe2 are reported. Comprehensive experiment and calculation proofs confirm that the moderate Fe doping can optimize the spin state of adjacent Co atoms, facilitating the formation of high-valence Co sites. This study proposes a novel perspective based on the doping induced spin state tuning to explain the formation mechanism of highly active OER sites and pioneers an interesting method for the modulation of advanced spin-related electrocatalysis. This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of HUST and Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics.
Link of the paper: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EE03500A