Recently, Research Group Led by Prof. Xie Xiaolin and Prof. Wang Yong published their research work entitled " One-pot synthesis of hyperbranched polymers via visible light regulated switchable catalysis " on Nature Communications.
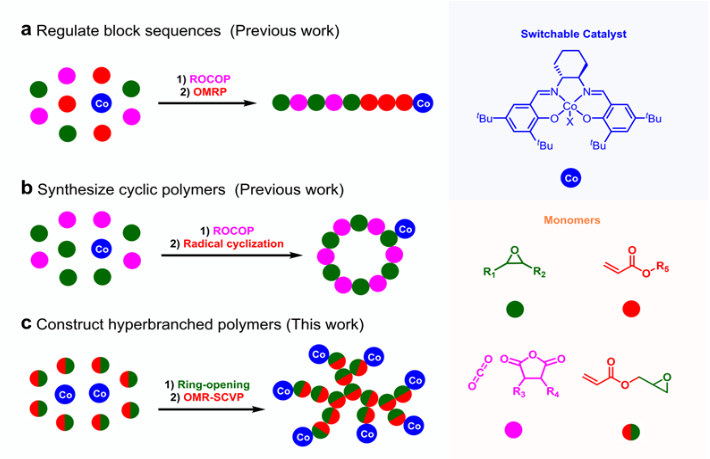
Switchable catalysis promises exceptional efficiency in synthesizing polymers with ever-increasing structural complexity. However, current achievements in such attempts are limited to constructing linear block copolymers. Here we report a visible light regulated switchable catalytic system capable of synthesizing hyperbranched polymers in a one-pot/two-stage procedure with commercial glycidyl acrylate (GA) as a heterofunctional monomer. Using (salen)CoIIICl (1) as the catalyst, the ring-opening reaction under a carbon monoxide atmosphere occurs with high regioselectivity (>99% at the methylene position), providing an alkoxycarbonyl cobalt acrylate intermediate (2a) during the first stage. Upon exposure to light, the reaction enters the second stage, wherein 2a serves as a polymerizable initiator for organometallic-mediated radical self-condensing vinyl polymerization (OMR-SCVP). Given the organocobalt chain-end functionality of the resulting hyperbranched poly(glycidyl acrylate) (hb-PGA), a further chain extension process gives access to a core-shell copolymer with brush-on-hyperbranched arm architecture. Notably, the post-modification with 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) affords a metal-free hb-PGA that simultaneously improves the toughness and glass transition temperature of epoxy thermosets, while maintaining their storage modulus.
Link to this paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37334-x